Monday, March 24, 2025
Introduction
An AC input UPS (Uninterruptable Power Source) is the most frequently used method of maintaining power to equipment during a temporary loss of power. It is placed in between the incoming AC source and the AC input to the product. When the AC power is available the rectifier and inverter circuits are bypassed.
In the event of a power outage, energy is drawn from the battery and converted into an AC voltage by an inverter. This keeps the equipment operating until the AC power is restored, an alternative source of power is provided or the battery is discharged. Once the AC power is resumed, the rectifier will charge the battery and the bypass circuit will again operate.
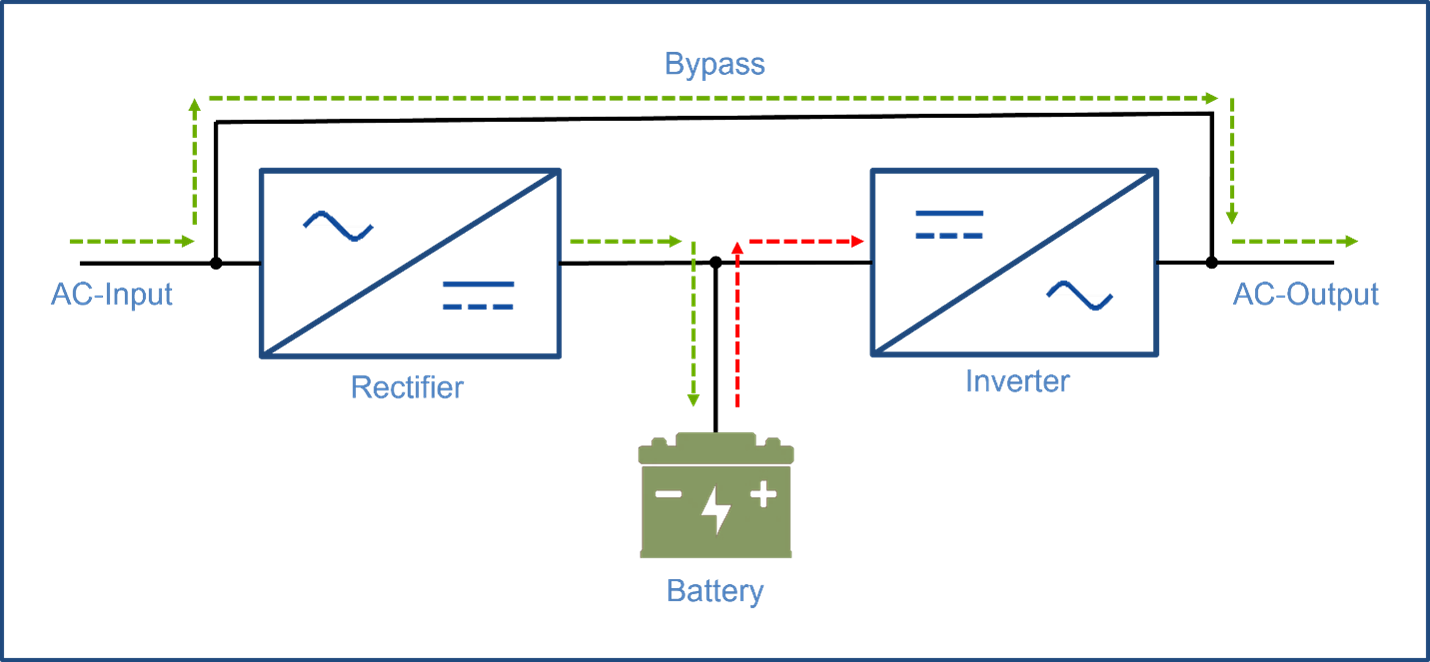
Figure 1: AC input UPS block diagram
A DC-UPS uninterruptible power system is also powered from an AC input and placed between the DC output of the power supply and the load. Under normal conditions it will deliver a DC voltage to the system load. In the event of a temporary loss of power, the DC-UPS will then draw DC power from the battery (or other DC source) maintaining power to the system load until the battery is discharged.
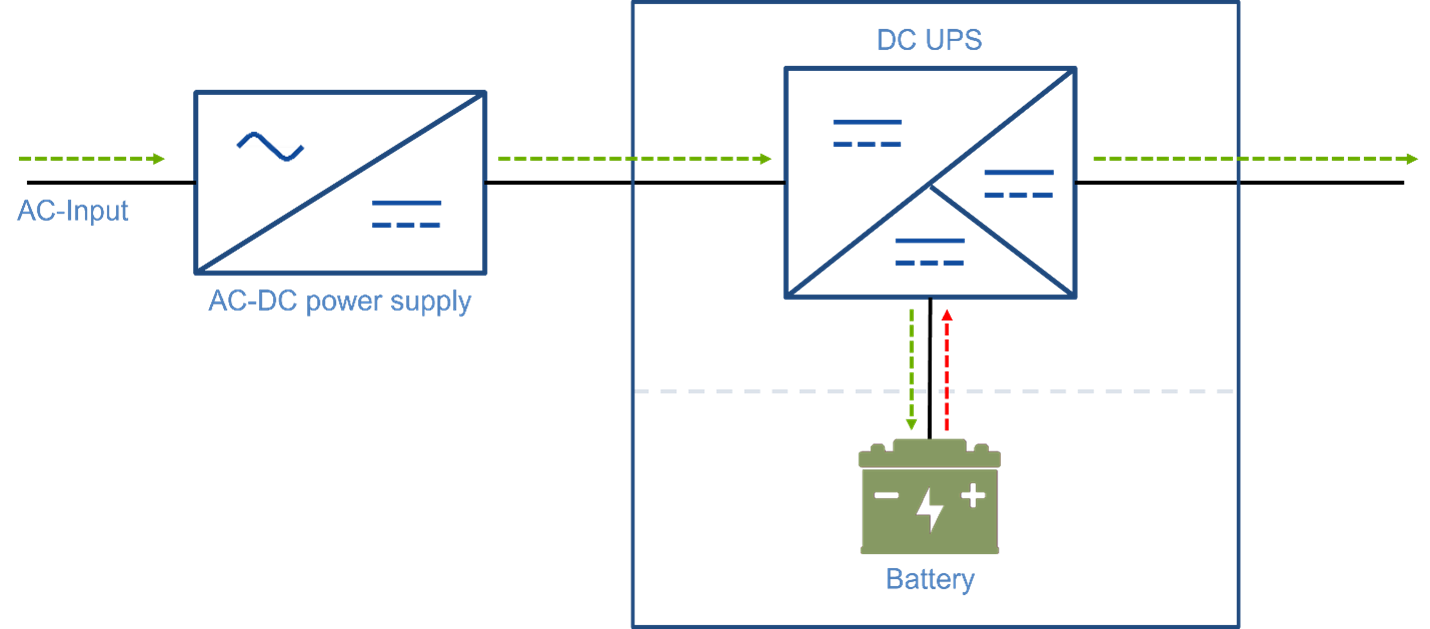
Figure 2: DC-UPS block diagram
Why consider DIN rail mount products?
Many industrial applications use AC-DC DIN rail mounted products. They are easy to click into place on a standardized bracket with minimal tools for installation and require no forced air cooling. A host of DIN accessory products are also available, including buffer (extended hold-up) modules, OR-ing diode solutions for redundant operation, EMC filters, DC-DC converters and the ability of a DC-UPS to provide protection against power loss.
- A DC-UPS has a greater operating efficiency - up to 98% - than a traditional UPS, saving energy and reducing waste power.
- It can operate with multiple battery technologies, including lead acid, nickel metal hydride, lithium-Ion and even super capacitors.
- Battery voltage ranges are much wider, allowing nominal levels from 10 – 58V for system flexibility.
- DC-UPS module can manage the health status of the battery by preventing deep discharging, enabling temperature-compensated charging, and monitoring the internal resistance through a user interface.
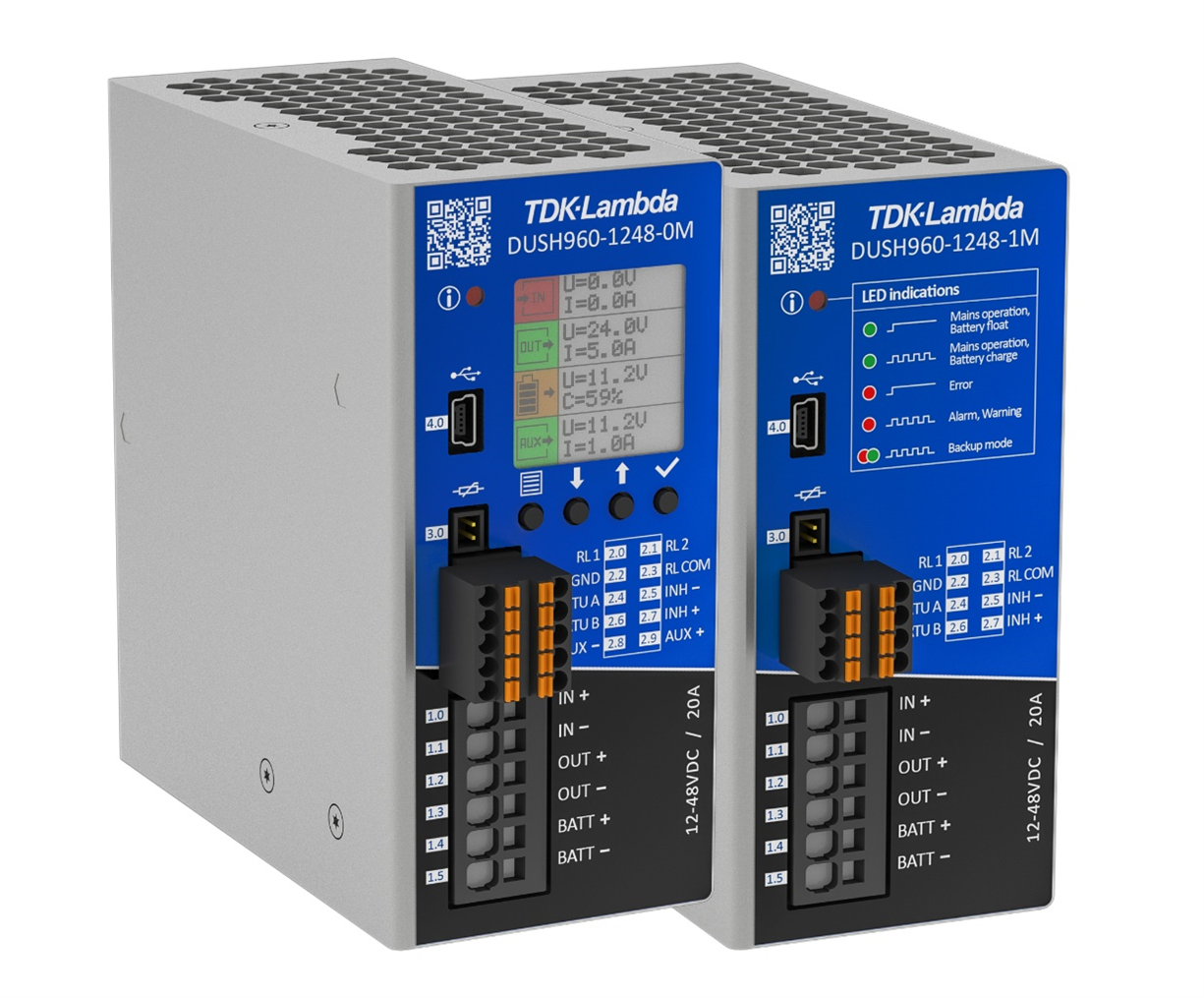

Figure 3 TDK-Lambda DUSH960-1248 DC UPS
Please do not hesitate to call or email TDK-Lambda Americas Technical Support or your local sales office if you have any questions regarding a power supply for your next project. https://www.us.lambda.tdk.com/contact/.