What are the advantages and disadvantages of using wide range input DC-DC converters?
Tuesday, December 3, 2024
Introduction:
DC-DC converters perform an essential function in electrical and electronic applications. They provide additional voltage sources powering circuitry that requires a higher, or lower, voltage level than the DC input source. That source voltage can be an AC-DC power supply, another DC-DC converter or a battery for portable applications.
The input range of a DC-DC converter is frequently stated as a ratio. A 48V telecom system may require a 36 to 72V input converter to operate on a battery during charge and discharge. This would be referred to as 2:1 or (2:1). For rail applications a converter maybe operate from 8.5 to 160Vdc input. In this case the converter would have an 18:1 input range.
Historical:
Twenty years ago the majority of DC-DC converters available on the commercial market had a 2:1 input range. 4.5 to 9V for a 5V nominal input, 9 to 18V (12V), 18 to 36V (24V) and 36 to 72V for a 48V nominal input.
Current technology:
Multiple efficiency improvements have been made. New ferrite core technologies, lower resistance MOSFETs, improved ceramic capacitors and integrated circuits, smaller components, advanced packaging and thermal management software have been introduced. This has allowed designers to offer smaller package sizes and/or wider input ranges.
This has brought some challenges during the inspection of surface mount component solder joints after the reflow process on these compact packages. TDK-Lambda has invested in computer controlled X-ray equipment to maintain quality and yield levels on their CCG series of 1.5W to 10W DC-DC converters (Figure 1), particularly when components are mounted under large components like the transformer.
Figure 1: 4:1 input range CCG DC-DC converters.
The advantages of wide range input DC-DC converters
Inventory reduction is probably the most recognized benefit. If product requires a 12V nominal input for one application and a 24V for another, one wide range model capable of operating from 9 - 36V simplifies inventory management. It allows higher volume purchasing with potentially a lower price and reduces part shortages and the need to carry two spare parts.
Automotive and battery applications
If DC input of the end application is subject to large voltage changes, like those seen in automotive cold start dips, a 4:1 converter will operate from 4.5 - 18V. Portable battery powered equipment may remain operating longer without needing to recharge.
Withstanding input voltage surges or dips
When the DC input is subject to input transients, very wide input voltage converters like those used on railroad applications can provide additional protection. TDK’s 20W rated PYD20 (Figure 2) has an 18:1 input range capable of operating from 8.5 to 160Vdc. The CN-B series (Figure 3) ranges from 30W to 300W and has a 43 to 160Vdc input
These can be beneficial in renewable energy equipment to counter wind / solar voltage variations.
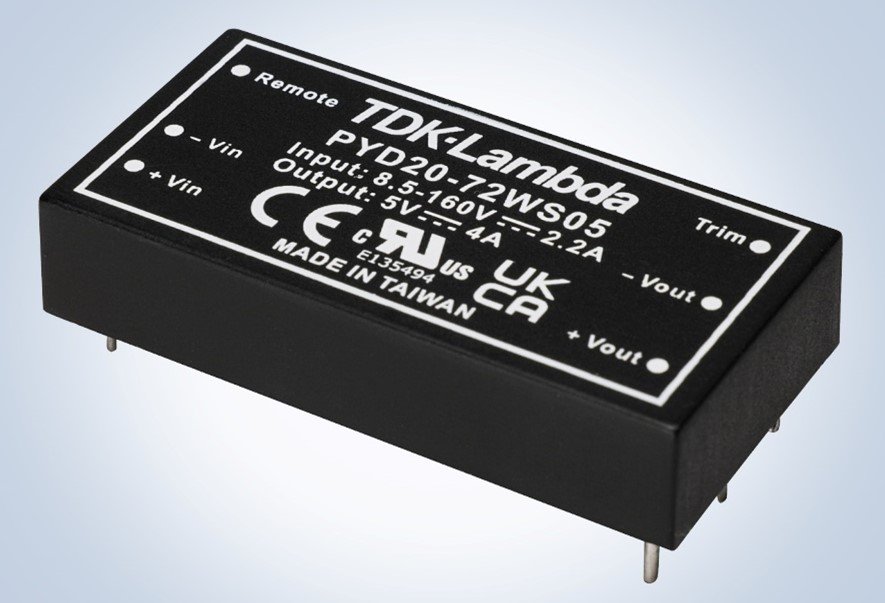

Figure 2: PYD20 8.5 to 160V input DC-DC converter

Figure 3: CN50B 43 to 160V DC-DC
The disadvantages of wide range input DC-DC converters
Cost
The cost of a using a wide input converter may be higher, due to the additional complexity.
Larger and more expensive external filtering components may be required for filtering and ripple reduction
Efficiency
The operating efficiency at the extremes of the rated input may be lower. At the low end of the input range the converter will draw more current. At the high end the switching pulse current of the converter will be narrower As the losses are resistive in nature, (power = I2R), the impact of the higher current value is effectively squared and the product’s efficiency decreases.
Size
Depending on the input voltage range and the output power, the DC-DC converter may be larger and consume more pcb area. This may apply to the external components too.
Non-isolated DC-DC converters
For higher power DC-DC converters, using non-isolated converters may provide a suitable solution. Unlike traditional board mount products, they have no isolation between the input and output. This may not be a concern as the AC-DC power supply has the safety barrier.

Figure 4: i1C 200W non-isolated buck-boost DC-DC converter
The i1C buck-boost converter (Figure 4) is rated at 200W and is packaged in the industry standard 1” x 1”.Power losses are minimized as the product is up to 98% efficient. These types of converters have a 4:1 input range and a wide output adjustment range (9.6 up to 28V) which it not usually found in isolated converters.
Please do not hesitate to call or email TDK-Lambda Americas Technical Support or your local sales office if you have any questions regarding a power supply for your next project. https://www.us.lambda.tdk.com/contact/